Logistics vs. Supply Chain Management: how do they differ?
Although logistics and supply chain management are closely connected, they are not the same thing.
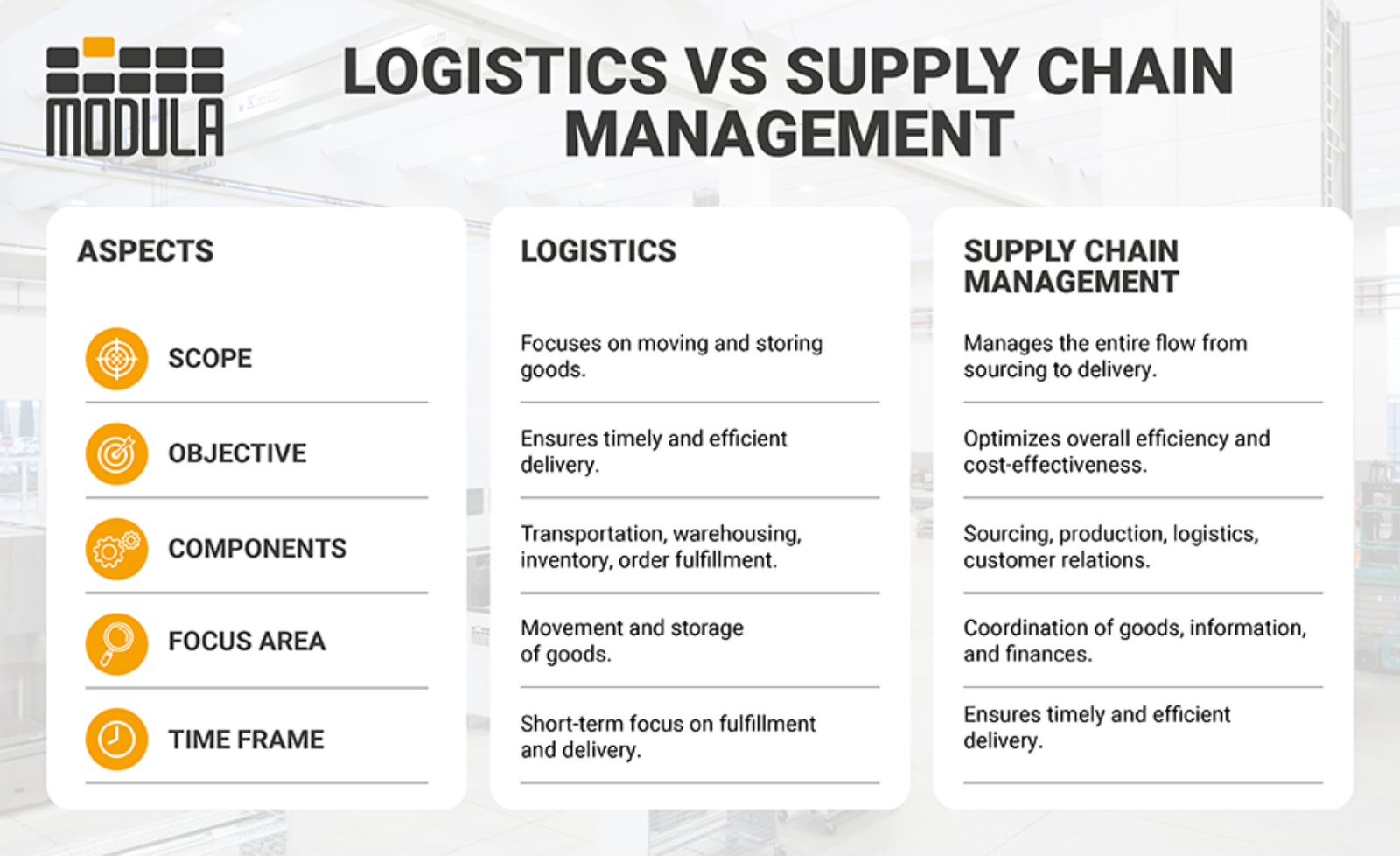
Logistics focuses on the storage and internal movement of goods, while Supply Chain Management takes a wider approach, covering every stage from sourcing raw materials to manufacturing, transportation, and final delivery.
Understanding the unique role of each discipline helps companies streamline operations, strengthen competitiveness, and improve profitability.
In this guide, you’ll learn how to:
- Define the responsibilities of logistics and supply chain management
- Understand the advantages of managing both effectively
- Discover how modern tools, such as a WMS, can help optimize performance across your business
What do logistics and Supply Chain Management mean?
Logistics and supply chain management (SCM) deal with organizing the efficient flow and storage of goods and services from their point of origin to their final destination.
This covers processes such as receiving shipments, managing stock, transportation, warehousing, and distribution to make sure products reach the right customer, at the right time.
What is logistics?
Logistics is a specific branch of supply chain management focused on planning, executing, and overseeing the storage and movement of goods, services, and related data.
Its main objective is to ensure that the right item is delivered to the right place, at the right moment, in the right condition, and cost.
Logistics is usually divided into two main categories:
- Inbound logistics: managing goods that arrive at a company.
- Outbound logistics: handling the delivery of products to customers.
What is Supply Chain Management?
Supply chain management is a broader concept that coordinates all activities across suppliers, manufacturers, distributors, and retailers to increase efficiency and meet customer expectations.
Supply chain managers work across different business functions and organizations to ensure products are produced, transported, and delivered on time, at the expected quality and cost.
Key distinctions between logistics and Supply Chain Management
Logistics emphasizes internal operations such as warehousing and transportation. It’s about controlling the flow of goods inside a company or between immediate business partners.
Supply chain management covers the entire lifecycle of a product—from sourcing raw materials through production, distribution, and final delivery to the end customer. It also relies heavily on collaboration between all stakeholders involved.
A simple way to look at it: logistics is like the engine moving parts inside a factory, while supply chain management supervises the whole assembly line—from raw material sourcing all the way to delivering the finished product to the consumer.
Logistics deals with the internal movement and storage of goods within the supply chain, while supply chain management oversees a wider set of activities, such as sorting, distribution, and sales.
Key logistical components in the supply chain
Supply chain logistics play a critical role in coordinating the movement of products and services. They ensure that every stage supports the smooth transfer of raw materials and finished goods through different phases of the supply chain.
The main components of supply chain logistics include:
- Inventory status: Monitoring stock in real time enables smarter business decisions. For instance, when warehouse managers have accurate visibility of inventory levels, they can adjust purchasing and production plans to avoid both shortages and overstock.
- Storage: Proper storage practices help maintain the right amount of goods at the right locations, balancing supply with demand to prevent understocking or excess inventory.
- Warehousing: This covers day-to-day warehouse activities such as receiving, storing, picking, packing, and shipping.
- Material handling: Involves the physical handling, movement, and safeguarding of goods throughout manufacturing, distribution, and delivery processes.
- Unitization: Consolidating smaller units into larger loads helps improve warehouse efficiency, streamline packaging and organization, and make handling and transportation easier.
- Inventory control: Combines storage and warehouse management strategies to regulate stock levels and product types. By using inventory management methods—such as the Economic Order Quantity (EOQ) model—companies can determine the optimal order quantity and replenishment timing, reducing carrying costs and minimizing the risk of surplus stock.
- Packaging: Proper packaging prevents damage during transit and can also strategically lower shipping costs.
- Transportation: Manages the movement of goods across the supply chain, either to the next facility or directly to customers. It involves selecting the most suitable vehicles—cars, trucks, trains, planes, or ships—based on route and cargo type.
Key advantages of effective logistics management
Because the movement of goods is directly tied to cash flow, managing logistics efficiently is essential for every business.
The way logistics are handled can greatly influence a company’s financial performance—either strengthening it or creating costly challenges.
- Greater supply chain visibility: Strong logistics management provides better transparency throughout the supply chain. This makes it easier for companies to control costs, identify efficiencies, spot potential problems, forecast demand, and capitalize on new opportunities—such as entering new markets or building stronger supplier relationships.
- Reduced operating expenses: By cutting shipping costs and optimizing warehouse space through proactive inventory management, logistics can lower overall overhead and streamline operations.
- Enhanced customer satisfaction: Fast and accurate order fulfillment leads to a better customer experience—an essential driver of customer loyalty. Satisfied customers often become brand advocates, sharing positive feedback through word of mouth and social media, which helps attract new clients and boosts brand visibility.
- Stronger inventory control: Accurate inventory tracking in real time reduces losses and prevents stock discrepancies. This is especially important considering that nearly one in four consumers has faced stockouts when trying to make a purchase. Proper logistics ensures precise stock counts and close monitoring of product movement and locations.
- Support for business growth: Reliable demand forecasting enables businesses to predict inventory requirements more accurately and optimize procurement and transportation. Applying best practices in logistics allows organizations to scale operations effectively to meet increasing customer demand.
- Greater flexibility and agility: Well-structured logistics systems allow companies to quickly respond to changing market conditions, seasonal demand shifts, or unforeseen disruptions. This flexibility provides a competitive advantage by ensuring service consistency and maintaining customer satisfaction.
Benefits of Effective Logistics Management: When logistics is managed properly, businesses can achieve higher efficiency, lower costs, and faster delivery times—factors that are essential for both competitiveness and customer satisfaction.
How Modula’s WMS can elevate your logistics and supply chain operations
A Warehouse Management System (WMS) is specialized software designed to help companies organize and control warehouse operations from the moment goods enter a facility until they are shipped out.
Implementing a WMS can transform logistics and supply chain performance by delivering several critical advantages:
- Greater inventory accuracy: With end-to-end tracking of each item, a WMS eliminates stock discrepancies, reduces the risk of overstock or shortages, and provides real-time visibility into stock levels, order progress, and productivity. This allows managers to quickly respond to operational issues.
- Optimized space utilization: By assigning storage locations according to item dimensions, weight, and frequency of access, a WMS maximizes warehouse capacity and reduces unnecessary overhead costs.
- Higher workforce productivity: A WMS directs pickers to the most efficient routes and pick points, cutting travel time and speeding up workflows. It can also prioritize tasks and allocate them based on staff availability, improving overall labor efficiency.
- Improved demand forecasting: Built-in analytics and reporting features allow managers to spot trends, anticipate fluctuations in demand, and make better-informed inventory decisions.
- Lower operating costs: By minimizing errors such as mispicks—which often result in costly returns or reshipments—a WMS helps reduce both labor expenses and waste.
- Regulatory compliance and streamlined documentation: A WMS automatically records inventory movements and generates shipping and customs documents, reducing manual work, minimizing errors, and ensuring compliance with regulations.
A Warehouse Management System (WMS) plays a vital role in strengthening logistics and supply chain performance.
To make operations even more efficient, companies can integrate their WMS with Modula’s Vertical Lift Modules (VLMs). These Automated Storage and Retrieval Systems (ASRS) increase storage density, minimize floor space requirements, and dramatically speed up retrieval times.
The result is faster and more accurate order fulfillment, along with higher productivity across warehouse activities.
Ideas for warehouse reorganization